Scrum can be quite beneficial for non-agile project managers looking to enhance their project management skills and adapt to more flexible and iterative approaches.
This post will give you a gentle introduction to Scrum and its various processes. Scrum is an agile framework that emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and iterative progress.
Unlike traditional project management, which often follows a linear and sequential approach, Scrum allows teams to work in short, focused cycles called sprints.
This iterative process helps teams to adapt quickly to changes and continuously improve their work.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is Agile methodology to tackle the projects
Unlike traditional project management methods that rely on detailed upfront planning, Scrum operates on the principle of iteration and continuous improvement.
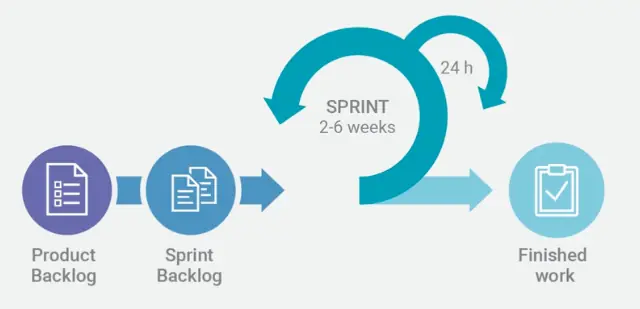
In Scrum, work is organized into short iterations known as “sprints,” typically lasting one to four weeks. During each sprint, the team focuses on delivering a small, tangible piece of the overall project, known as an increment.
Scrum is a practical method to work productively with a dedicated team.
The core of Scrum consists of roles, ceremonies, and lists.
- There are clear roles so everybody knows where he/she stands
- fixed ceremonies in which team comes together.
- few handy lists that replace extensive, highly-inefficient plans
Scrum Roles
Scrum has three distinctive roles
- Product Owner
- Scrum Master
- Scrum Team

Product Owner
Product owner “owns” the product or the content. He is in close contact with the customer and translates customer’s requirements into clear assignment to the team.
The Product Owner monitors the job, the priorities, and the preconditions and makes decisions where necessary.
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master guides the team so that the process runs smoothly.
The Scrum Master is therefore responsible for the quality of the process: ensuring that the Development Team takes the right steps and that ceremonies take place in the right way and at the right time.
Scrum Team
It contains professionals from various disciplines, such as business analysts, designers, and programmers, to take care of the tasks.
Scrum Team does not have a Project Manager. This means that the team members decide together how they want to carry out the tasks and divide the work.
Four Scrum Ceremonies
Scrum ceremonies occur at four different types of team meetings.
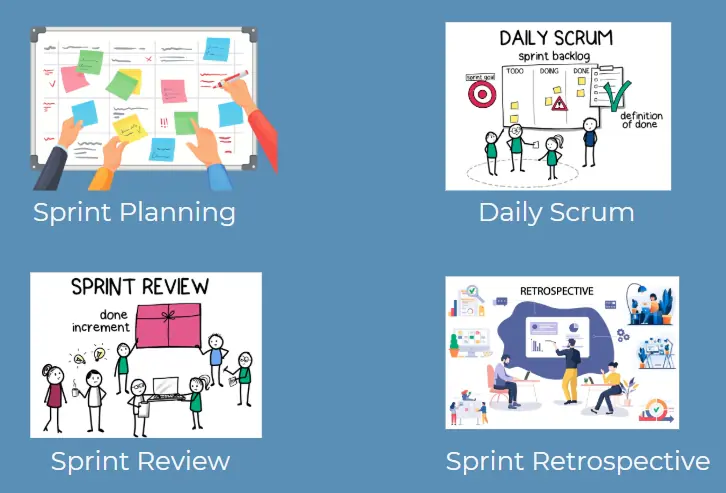
Sprint Planning
Every new sprint starts with a sprint planning meeting, in which the team determines how it can achieve the most important goals for this sprint.
The important goals are taken from Product Backlog – a list of customer requirements.
Daily Scrum
Daily Scrum are stand up meetings. These meetings are regularly held.
These are short interim discussions of no more than fifteen minutes, during which the team members tell each other the progress of the tasks.
Sprint Review
At the end of every sprint, the team presents everything that was made in this sprint to the Product Owner. This is called the sprint review.
Stakeholders provide feedback, and the Product Backlog is adjusted as needed.
Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective takes place after the Sprint Review and is a reflective event. The Scrum Team inspects its processes and identifies improvements for the next Sprint.
Four Scrum Lists
The lists are indispensable part of Scrum. The four scrum lists are nothing more than visual aids. In Scrum, you usually display the lists on flip charts with Post-it Notes, that show what the team is working on.
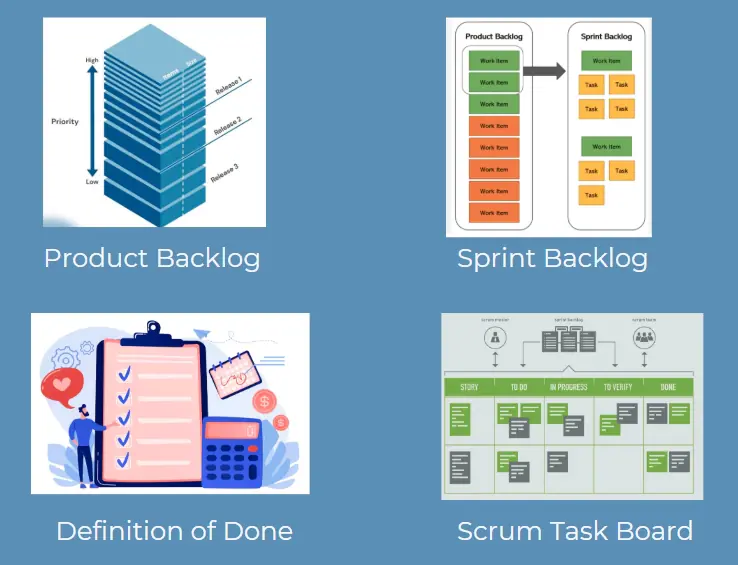
Product Backlog
Product Backlog is the overview with all requirements for the entire project.
With Scrum, you no longer have to write an extensive long-term plan, but the Product Owner makes an inventory of the components that must be worked out for this project.
Sprint Backlog
At the start of every sprint, the Development Team selects, along with the Product Owner, the items from the Product Backlog that the team will work in the coming sprint.
This list is called as Sprint Backlog
Definition of Done
These are the requirements that a team must fulfill to be considered “done.”
The “definition of done” answers the question: What exactly will be finished and achieved at the end of the sprint, and what does that look like?
Scrum Task Board
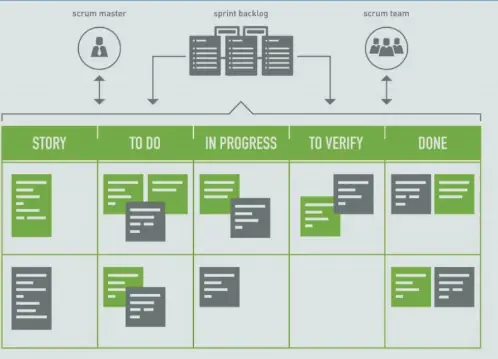
Scrum board shows the items of the Sprint Backlog and consists of the columns “to do,” “busy,” and “done.” The Scrum board can be digital but is usually made on a physical whiteboard or flip chart.
It visually shows the progress of sprint activities
Scrum Metrics
Scrum metrics are instruments for measuring the Scrum process. Scrum metrics focus on the value that is delivered to the customer.
Commonly used metrics in Scrum are:
- Lead Time
- Cycle Time
- Velocity
- Burndown chart
- Story Points
- Defects per Sprint
These metrics are used to track progress, identify issues, and course correct as needed. All Scrum metrics should be closely monitored to ensure success of a project.
Lead Time
Lead time is elapsed time between customer’s order of a product and its final completion as per the customer requirements. This measures how long it takes to get the things done and is key metric to track efficiency of a team in terms of its ability to get things done.
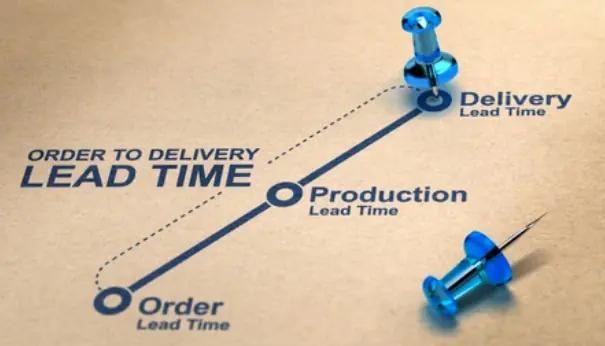
Cycle Time
Cycle time is a length of a time it takes to complete one full cycle of a task. It includes lead time, and can help identify areas of improvement. It also helps to track Work In Process inventory – a very useful parameter to reduce wastes in a process.
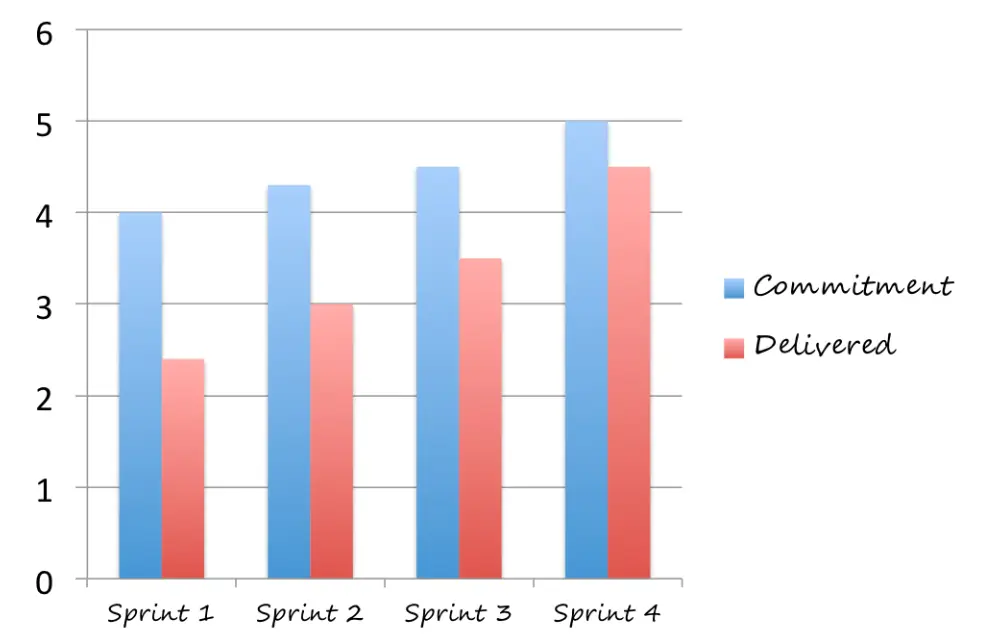
Velocity
It measures amount of work team can complete within a specific time frame. The teams’s velocity can fluctuate over time due to factors such as team composition, scope changes, or external factors that impact their ability to work efficiently.
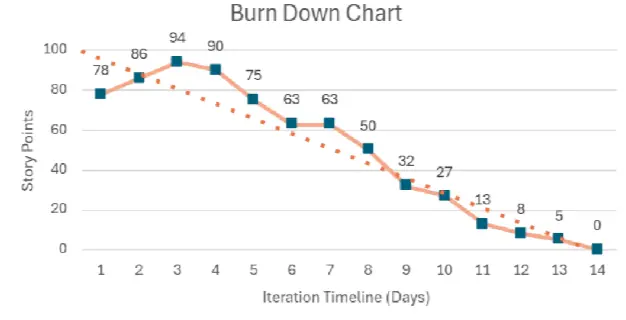
Burn Down Chart
Burn down chart gets its name because the number of tasks, or work hours will go down as scrum team burns through the activities in a project phase.
The project manager starts at the upper left-hand corner of the chart, before any development work is completed and as features are completed and burned down the project manager tracks that progress with a simple line chart.
Story Points
Story points are unit of measure to estimate the relative size and complexity of user stories or other units of work. They are a way of assigning a numerical values to a piece of work based on the effort required to complete it.
Defects Per Sprint
Defects per sprint measures number of defects or bugs found during single sprint or iteration. It shows the quality of the work being done by the development team, and help the team to identify areas for improvements.
Benefits of Scrum
- Reduced Time to Market of a Product: With Scrum, product increments are delivered as fast as possible. Therefore the “Time-to-Market” of a product can be drastically shortened.
- Delivering higher quality products to customer: By asking customers and other stakeholders for their opinion during every sprint review, you never lose sight of the customers requirements and expectations.
- Scrum allows to explore uncertain and complex projects: You can quickly assemble a Scrum Team to work on several sprints. After a few weeks, you’ll know whether a new product is feasible. If not, better luck next time, at least you learned something. This is far efficeint approach than long and extensive documentation done by several external consultants.
- Scrum gives team more control over entire product creation process: This control is achieved through its iterative and incremental approach, which allows teams to respond rapidly and effectively to changes.
- Flexible to Change: Scrum allows quick reaction to changes in requirements generated by customer needs or market developments. This methodology is designed to adapt to the changing requirements that complex projects demands.
Summary
The difference between Scrum and other agile methods is that it’s the easiest and most flexible method to implement.
Scrum doesn’t require any advanced mathematics or rocket science.
The core of a scrum are clear roles, fixed ceremonies in which team comes together, few handy lists that replace extensive, highly-inefficient plans and very easy to interpret scrum metrics to track the work.
References
Agile Practice Guide – PMI Practice Guide
Do you want to Master the World’s Most Popular Project Management Tool?
Check out my 18 Hours LIVE Online Course on Microsoft Projects.
Did you know that nearly 60% of Project Management roles posted on LinkedIn require Microsoft Projects skills?
Microsoft Projects, a project management software in use since 1984, stands out as the most established and widely utilized tool across various industries.
Major players like Fortune 500 companies rely on this software to propel their projects forward. Stay ahead of the curve. Acquire this valuable skill now and set yourself apart from other project managers.
For additional information:
Visit the course web-page:pmfornonpm.in/new-courses/




